Just like a living journey, every product walks its own path, rising, thriving, and eventually stepping aside. This journey is known as the product life cycle (PLC), a vital concept every business must understand to stay competitive and relevant.
So, what is product life cycle? It's a business concept that outlines the various phases a product goes through, from its market introduction to its eventual withdrawal. Understanding the product life cycle stages allows businesses to make informed decisions that extend a product’s profitability and relevance in the marketplace.
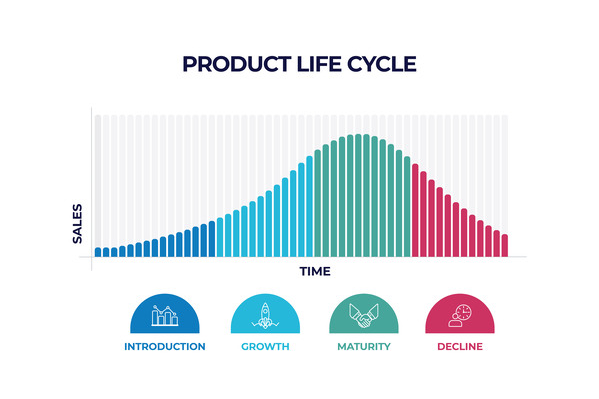
A product typically moves through four key stages: Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline. Each stage demands a unique approach in terms of strategy, investment, and marketing.
Surprisingly, many businesses overlook the significance of the product life cycle. According to Harvard Business School Professor Clayton Christensen, a staggering 95% of new products fail within their first year. This statistic alone underscores how critical it is to grasp the full picture of a product's journey.
Why is mastering the product life cycle so important? The answer is simple, it empowers businesses not just to survive but to evolve, extend their product’s presence in the market, and uncover new growth opportunities.
In this article, you'll dive deep into the meaning of product life cycle, explore detailed product life cycle examples, and uncover practical strategies to manage them successfully.
The Four Stages of the Product Life Cycle
Understanding the product life cycle stages is the first step toward successful lifecycle management. Each stage comes with its own opportunities and hurdles, requiring thoughtful strategy and agile execution.
1. Introduction Stage
This is where the journey begins. During the introduction stage, a product was newly launched onto the market. It’s often marked by high marketing and production costs, with relatively low sales due to limited consumer awareness.
The main goal here is to build brand awareness and generate interest. A well-crafted marketing campaign, broad distribution channels, and clear communication about the product’s benefits are essential. Gathering feedback from early costumers helps refine both the product and future marketing efforts.
Educating the market on what makes the product unique is also crucial. This stage sets the foundation for everything that follows.
2. Growth Stage
Once the market starts to accept and adopt the product, it enters the growth phase, where sales rise rapidly. This is a golden period, but it also invites competition.
To maintain momentum, businesses should focus on improving product features, expanding their distribution network, and enhancing marketing effectiveness. Price adjustments, promotional offers, and loyalty incentives can help attract a broader customer base and encourage repeat purchases.
This is the time to scale operations efficiently while maintaining quality and brand consistency.
3. Maturity Stage
During this stage, the product reaches peak market penetration. Sales may stabilize, and growth slows as the market becomes saturated. Competition is fierce, and maintaining profit margins becomes more challenging.
Differentiation becomes key during this phase. Companies must innovate, whether through product enhancements, pricing strategies, or exploring untapped markets. Marketing efforts should target specific customer segments or geographic regions to breathe new life into the product.
Operational efficiency also plays a major role in sustaining profitability during this stage.
4. Decline Stage
Eventually, most products enter the decline stage, marked by falling sales and reduced demand. This can happen due to shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, or stronger competition.
At this point, companies must decide whether to revitalize the product through innovation, reposition it in a niche market, reduce costs, or discontinue it altogether. Strategic decisions based on thorough market analysis will determine the best course of action.
What Influences a Product’s Life Cycle?
The length and success of a product life cycle are not solely determined by internal strategy. External factors play a major role, too. Let’s explore the key elements that impact how fast or slow a product moves through its lifecycle.

1. Market Trends
Changes in consumer behavior and preferences can either extend or shorten a product’s life. For example, rising environmental consciousness has boosted demand for sustainable products, while traditional, non-eco-friendly alternatives see shorter lifespans.
Businesses that adapt swiftly to such trends can prolong their product market presence and even open new revenue streams.
2. Technological Advancements
Innovation in technology can disrupt entire industries overnight. Digital transformation, for instance, has accelerated the product life cycle of examples across electronics, software, and even services.
Companies investing in research and development (R&D) are more likely to keep their offerings relevant and competitive.
3. Competitive Landscape
New entrants or aggressive moves by existing competitors can cut short a product’s growth or maturity phase. On the flip side, strong differentiation allows some brands to enjoy extended periods of success.
Ongoing competitor analysis and adaptive marketing strategies are vital for staying ahead in a crowded marketplace.
Strategies to Manage the Product Life Cycle
Managing the product life cycle stages isn't just about reacting to change. It requires forward-thinking, strategic planning, and continuous improvement. Here’s how to stay one step ahead:

1. Product Development
Aligning product creation with real market needs is fundamental. Before launching, conduct deep market research to understand what your target audience wants, not just now, but in the near future.
This helps you build adaptable, relevant products with lasting value.
2. Launch Strategy
An impactful product launch begins with knowing your audience. Develop segmented marketing strategies and choose the right channels to communicate your message.
Use pricing strategies that spark curiosity and encourage early adoption, while designing campaigns that build long-term brand resonance.
3. Managing the Growth Stage
During the growth phase, continuous monitoring of market responses is essential. Expanding distribution, boosting marketing budgets, and adding new features can help sustain momentum.
Exploring new geographic regions or customer segments can also accelerate growth and increased market penetration.
4. Optimizing the Maturity Phase
In the maturity phase, the focus shifts to retaining market share and maximizing profitability. Streamlining operations, modifying products to suit different segments, and using dynamic pricing strategies can help maintain competitiveness.
Targeted marketing and loyalty programs play a big role in keeping customers engaged and encouraging repeat purchases.
5. Navigating the Decline Stage
When signs of decline appear, don’t wait. Decide whether to reduce operational costs and maximize remaining profits, reposition the product to niche markets, reinvest in innovation to refresh the offering, or gracefully retire the product to focus on newer innovations
Each decision must be grounded in solid data and aligned with long-term business goals.
6. Innovation and Diversification
Insights gained from managing current products can guide R&D initiatives and diversification strategies. By identifying new opportunities, companies can introduce innovative products that complement their existing portfolio and strengthen their market position.
Conclusion
From launch to retirement, each stage of the product life cycle presents unique opportunities and challenges. Understanding and applying the right strategies at each phase can significantly enhance a product’s performance and longevity in the market.
By leveraging insights from the product life cycle stages, companies can become more proactive in managing their product portfolios, not just reacting to changes, but anticipating and shaping them.
Moreover, as products move through growth and maturity, operational efficiency becomes increasingly important. That’s where advanced solutions like IoT Smart Manufacturing from Telkomsel Enterprise come into play.
These digital tools enable real-time monitoring of machine performance, production output, and warehouse activities. Features like Smart Manufacturing OEE, CMMS, and Smart Warehouse allow companies to digitize operations, improve inventory accuracy, speed up delivery times, and reduce human errors.
Interested in transforming your manufacturing processes? Discover how IoT-based smart solutions can boost your productivity and support your product’s journey through every product life cycle. Contact us today to learn more!