Bringing predictive maintenance into manufacturing asset management isn’t just an upgrade, but it’s a revolution in how modern industry operates.
Unexpected machine failures don’t just disrupt production, but they drain profits. For manufacturers managing hundreds of critical assets, even a few minutes of unplanned downtime can translate into massive losses. That's why predictive maintenance is rapidly becoming a game-changer in manufacturing asset management.
Unlike traditional maintenance strategies that rely on routine schedules or wait for breakdowns, predictive maintenance harnesses real-time data, sensors, and AI-powered analytics to forecast equipment failures before they happen. This approach empowers manufacturers to prevent costly interruptions, extend asset lifespans, and streamline operations with precision.
According to research by the International Society of Automation (ISA), unplanned downtime can slash as much as 15% of annual production output. With predictive maintenance, companies gain visibility into machine health and make data-driven decisions that boost reliability, safety, and performance across the board.
What Is Predictive Maintenance?
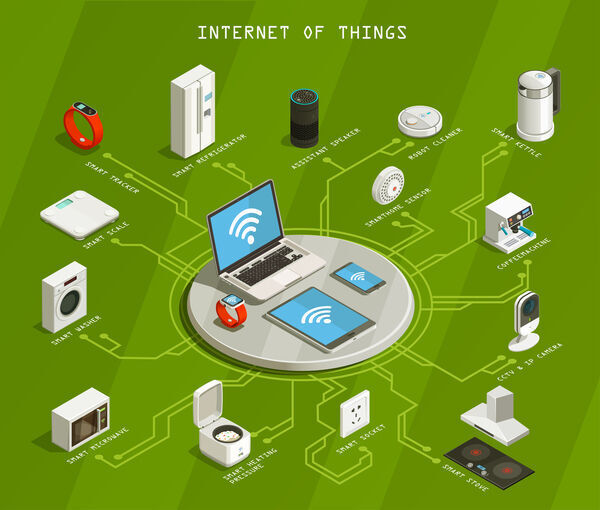
Predictive maintenance is a proactive maintenance approach that leverages technologies like IoT sensors, AI, and machine learning to monitor equipment condition and performance in real-time. Rather than relying on scheduled maintenance or waiting for equipment failure, predictive systems anticipate issues before they escalate.
This method enables manufacturing asset management teams to make smarter decisions, intervening only, when necessary, thus optimizing labor, minimizing downtime, and reducing maintenance costs.
How Predictive Maintenance Works
The core principle behind predictive maintenance lies in continuous monitoring and intelligent analysis. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it operates:
1. Data Collection
IoT sensors are installed on critical equipment to monitor key parameters such as temperature, vibration, pressure, humidity, and electrical flow. These sensors transmit real-time data to centralized systems for processing.
2. Data Analysis
Real-time and historical data are analyzed using AI-powered algorithms and machine learning to detect anomalies and patterns that indicate potential failures.
3. Predictive Modeling
Machine learning models are trained on historical and real-time data to forecast when specific components might fail. These models are continuously refined to improve accuracy over time.
4. Alert Generation & Maintenance Planning
When a potential issue is identified, the system generates alerts for maintenance teams. This allows engineers to plan interventions during scheduled downtimes, avoiding costly disruptions.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing Asset Management
Adopting predictive maintenance within manufacturing asset management brings transformative results. Here are some of the most impactful advantages:
1. Reduce Downtime
By identifying early signs of wear or malfunction, predictive maintenance enables timely repairs before breakdowns occur. This minimizes costly interruptions in production schedules.
2. Lower Maintenance Costs
High maintenance costs often pose a significant challenge for many manufacturers. Predictive maintenance helps reduce these expenses in several ways:
-
Early problem detection: By identifying issues early, repairs can be made before problems escalate into costly breakdowns.
-
Reducing unnecessary maintenance: Unlike preventive maintenance that occurs on fixed schedules regardless of equipment condition, predictive maintenance is performed only when needed, based on actual machine health. This avoids wasteful maintenance activities.
-
Optimizing resources: Predictive maintenance enables better planning of resources, including labor and spare parts. Knowing exactly when a machine needs service helps companies allocate their maintenance workforce and inventory more efficiently.
3. Extend Equipment Lifespan
Timely interventions prevent excessive wear and tear, allowing machines to operate in optimal condition for longer, boosting ROI on manufacturing assets.
4. Improve Workplace Safety
Detecting and resolving equipment issues early helps avoid accidents and injuries caused by malfunctioning machines, supporting a safer work environment.
5. Increase Operational Efficiency
With fewer breakdowns and optimized maintenance planning, production lines run more smoothly and consistently, improving overall plant performance.
6. Enhance Asset Reliability
Predictive maintenance ensures that each piece of equipment operates as intended, leading to more consistent output and fewer quality issues.
Challenges in Implementing Predictive Maintenance
Despite its advantages, predictive maintenance does come with some challenges:
-
Data Quality and Availability: Accurate predictions depend on high-quality data from well-calibrated sensors. Poor data quality or gaps can lead to incorrect forecasts.
-
System Integration Complexity: Integrating various technologies such as IoT devices, cloud platforms, and analytics tools. It requires a structured approach and robust integration frameworks.
Real-World Applications of Predictive Maintenance Across Industries
Predictive maintenance can be applied in various industrial sectors, from manufacturing, energy, transportation, to health. Here are some examples of its applications:
1. Manufacturing
Manufacturers deploy predictive maintenance to monitor CNC machines, robotic arms, and assembly line equipment. By analyzing real-time data on component wear or motor performance, they can reduce breakdowns and improve throughput.
2. Energy
Power plants and renewable energy sites use predictive maintenance to maintain turbines, generators, and power distribution systems. Remote sensors detect anomalies, reducing service disruptions, and maximizing uptime.
3. Transportation
Airlines, railway companies, and logistics providers install sensors on vehicles and equipment to monitor engine health, tire pressure, and brake systems, preventing accidents and delays.
4. Oil & Gas
Given the high-risk environments and remote locations, predictive maintenance helps detect issues in pumps, pipelines, and compressors before they cause costly failures or environmental damage.
5. Healthcare
Hospitals utilize predictive maintenance to ensure critical medical equipment like MRI scanners and ventilators function reliably, minimizing service interruptions and enhancing patient care.
Conclusion
Predictive maintenance is revolutionizing how industries manage their physical assets. By combining IoT, data analytics, and machine learning, it offers a smarter, more efficient way to maintain equipment and optimize manufacturing asset management.
From cutting downtime and reducing costs to extending equipment life and enhancing safety, the benefits are substantial. While implementation comes with technical challenges, the return on investment makes it a strategic priority for forward-thinking manufacturers.
If you're looking to integrate predictive maintenance into your operations, partnering with experienced Internet of Things (IoT) solutions by Telkomsel Enterprise can streamline adoption and maximize value.
Ready to transform your asset management strategy? Take the next step toward smarter, data-driven maintenance. Contact us today to explore how our IoT-enabled predictive maintenance solutions can enhance your manufacturing asset management and drive long-term success.