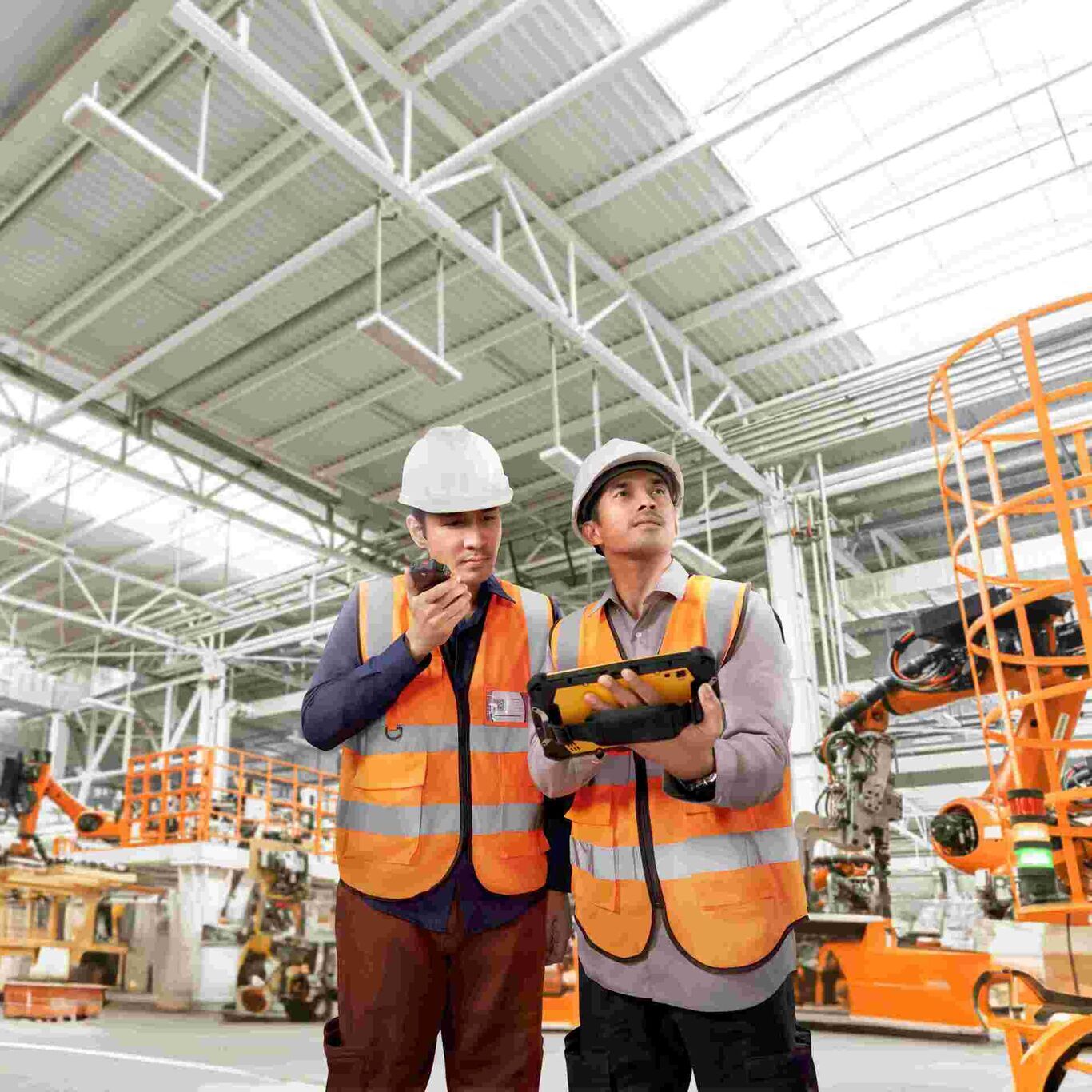
Fast and reliable communication is a critical factor in field operations such as logistics, construction, security services, and large-scale events. To ensure seamless coordination, Handy Talkies (HTs) remain a trusted communication device thanks to their simplicity, durability, and instant response.
As communication technology continues to evolve, handy talkies are now divided into two primary categories, which are analog and digital HTs. Understanding the differences between analog and digital handy talkies will help your company choose the most effective communication solution tailored to operational needs, scale, and budget.
What is a Handy Talky (HT)?
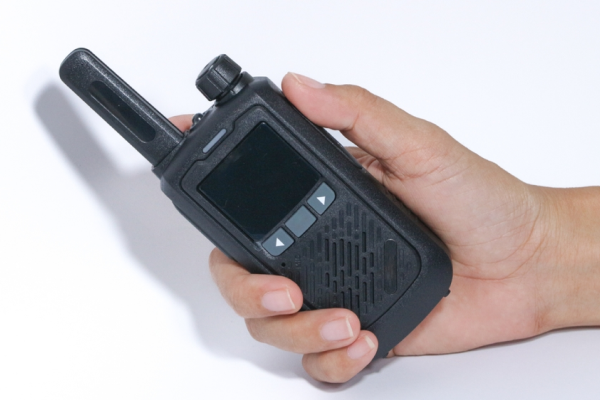
A Handy Talky (HT) is a two-way radio that enables direct, real-time communication using radio frequencies without relying on cellular networks or internet connectivity. Often referred to as analog and digital two-way radios, these devices are designed for instant coordination within a specific coverage area using a simple push-to-talk (PTT) button.
The main advantages of handy talkies include rapid response time, ease of use, and rugged construction that can withstand demanding field conditions. These strengths make HTs indispensable for teams that require uninterrupted communication in dynamic environments.
Understanding Analog HTs and Digital HTs
Based on their underlying technology, handy talkies can be classified into two types:
Analog HTs: Analog handy talkies use conventional radio communication technology that transmits voice signals in analog form. This technology has been widely used for decades and is known for its straightforward operation, affordability, and ease of setup.
HT digital: Digital handy talkies convert voice into digital data before transmission. By leveraging digital signal processing, digital HTs deliver more consistent audio quality and support a wide range of advanced features that are not possible with analog systems.
Main Comparisons of Analog and Digital HTs
The differences between analog and digital two-way radios become clearer when compared across key operational aspects:
Signal Reception
Analog HTs experience a gradual decline in audio clarity as signal strength weakens. Digital HTs, on the other hand, maintain clear sound quality up to a certain threshold before the connection drops completely.
Voice Encoding Technology
Analog HTs transmit voice signals directly. Digital HTs use codecs to compress and encode audio, allowing more efficient use of bandwidth and reduced interference.
Frequency Programming
Analog HTs are relatively simple to configure. Digital HTs require specialized software but offer higher precision, flexibility, and centralized control.
Communication Security
Analog communications are easier to intercept, making them less secure. Digital HTs support encryption, ensuring confidential and protected communication.
Audio Quality at Maximum Range
Digital two-way radio excels by delivering clear audio as long as the signal remains within coverage. Analog two-way radio tends to produce noise and distortion at long distances.
Compatibility
Analog HTs are generally compatible across different brands and models. Digital HTs often depend on specific standards or manufacturers.
Additional Features and Functions
Digital HTs offer advanced features such as text messaging, user ID display, GPS tracking, and group management. Analog HTs are typically limited to voice communication only.
User Capacity per Channel
Digital technology enables more users on a single channel through time-slotting techniques, increasing channel efficiency.
Licensing and Regulation
Both analog and digital HTs require frequency of licensing in accordance with government regulations. However, digital systems allow easier centralized monitoring and user control.
Price and Cost Efficiency
Analog HTs are more affordable upfront. Digital HTs involve higher initial investment but deliver better long-term efficiency and scalability.
How Analog and Digital Handy Talkies Work?
Although both function as two-way radios, analog and digital handy talkies operate using fundamentally different mechanisms. These differences directly impact sound quality, frequency efficiency, and communication stability.
How Analog HTs Work
Analog HTs operate using continuous signal transmission. When a user speaks, the microphone captures the voice and converts it into an analog electrical signal that mirrors the sound waves. This signal is then modulated using frequency modulation (FM) and transmitted via an antenna as radio waves.
On the receiving end, the radio waves are captured by the antenna, converted back into electrical signals, amplified, and played through the speaker as an audible sound.
Because the signal is continuous, analog audio quality is heavily affected by distance, environmental conditions, and frequency interference. As the distance increases, the sound becomes weaker and more susceptible to noise and distortion.
How Digital HTs Work
Digital HTs follow a more advanced yet efficient process. When a user speaks, the voice is first converted into an electrical signal and then processed by a vocoder (voice encoder) to transform it into digital data. This data is compressed to optimize bandwidth usage.
The compressed digital data is packaged into packets and transmitted using digital modulation techniques. On the receiving side, the data packets are reconstructed, verified for integrity, and decoded back into audible sound through the speaker.
Unlike analog systems, digital HTs maintain clear audio until the signal drops below the minimum threshold. Additionally, digital architecture enables advanced features such as encryption, user identification, and efficient channel management.
Which Is Better: Digital or Analog HTs?
The answer depends on your operational requirements. Analog HTs are ideal for simple communication needs with limited budgets and minimal security concerns. Digital HTs, however, are better suited for large-scale operations that demand wider coverage, stable audio quality, enhanced security, and advanced functionality.
For companies with high mobility and complex coordination needs, digital communication technology delivers greater value and efficiency. One example is Touch to Talk from Telkomsel Enterprise, a smart walkie-talkie solution powered by GSM technology and supported by Telkomsel’s extensive network coverage.
This solution enables instant communication not only through voice, but also via messages, images, and even video, all within a single multifunctional device.
With Touch to Talk, your organization can maximize field coordination without worrying about distance or network limitations. It’s time to elevate your team communication, rely on Touch to Talk from Telkomsel Enterprise for faster, safer, and more efficient coordination.
For more information on how Touch to Talk can support your business needs, start your consultation with Telkomsel Enterprise here.